IMMERSIVE
Set
집합의 정의는 유한하고 구분되는 객체들의 그룹이다. 집합은 가장 근간이 되는 자료 구조중 하나이다. 일반적으로 표현하면 프로그래밍에서 집합은 정렬되지 않은 유일한(중복되지 않는) 항목들의 그룹이다. 집합의 대표적인 특징은
- 순서가 없다.
- 중복이 없다.
라는 것이다.
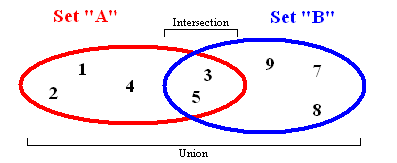
집합의 예시로는
정수집합: {1,2,3,4} 부분집합: {}, {1}, {2}, {3}, {4}, {1, 2}, {1, 3} ... {2, 3, 4}
위와 같은 정수집합이 대표적이다. 집합은 O(1) 상수 시간에 유일한 항목을 확인하고 추가할 수 있기 때문에 중요하다. 이번 예제에서는 집합의 가장 대표적인 연산들을 구현해보도록 하겠다.
구현할 기능
- add: 집합에 값을 넣음
- remove: 집합에서 값을 제거
- contain: 집합에 특정한 값이 있는지 확인
- intersection: 교집합
- union: 합집합
- difference: 차집합
구현
class Set {
constructor(...value) {
this.item = value;
}
// 값 추가
add(value) {
if (!this.item.includes(value)) {
this.item.push(value);
}
}
// 값 확인
contain(value) {
return this.item.includes(value);
}
// 값 제거
remove(value) {
if (this.contain(value)) {
this.item = this.item.filter((eachValue) => eachValue != value)
} else {
return "값이 없습니다";
}
}
// 교집합
intersection(otherSet) {
let intersectionResult;
intersectionResult = this.item.filter((eachItem) => {
return otherSet.item.includes(eachItem);
});
return new Set(...intersectionResult);
}
// 합집합
union(otherSet) {
let unionResult = [...this.item];
otherSet.item.forEach((eachItem) => {
if (!unionResult.includes(eachItem)) {
unionResult.push(eachItem);
}
})
return new Set(...unionResult);
}
// 차집합
difference(otherSet) {
let differenceResult = this.item.filter((eachItem) => {
return !otherSet.item.includes(eachItem);
});
return new Set(...differenceResult);
}
}
const a = new Set();
const b = new Set();
a.add(1);
a.add(2);
a.add(3);
a.add(4);
a.add(6);
a.add(7);
a.add(8);
a.add(9);
b.add(3)
b.add(4)
b.add(5)
b.add(6)
b.add(7)
const difference = a.difference(b);
const union = a.union(b);
const intersection = a.intersection(b);
console.log(a);
// Set { item: [1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9] }
console.log(b);
// Set { item: [ 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ] }
console.log(1, union);
// 1 Set { item: [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 5 ] }
console.log(2, intersection);
// 2 Set { item: [ 3, 4, 6, 7 ] }
console.log(3, difference);
// 3 Set { item: [ 1, 2, 8, 9 ] }
정리
집합은 정렬되지 않은 유일한 항목들을 나타내는 근간이 되는 자료구조이다. 자바스크립트 내부에 Set이라는 객체 자료형이 추가되기도 했다. 자바스크립트에 추가된 Set을 사용하면 집합 자료구조를 사용할 수 있다. 위의 예제는 집합의 개념을 코드로 구현해 본 것이라 생각하면된다. 소개된 내용이 집합의 전부는 아니지만, 집합의 가장 핵심이 되는 내용은 순서가 없고, 중복이 없다는 것이다.